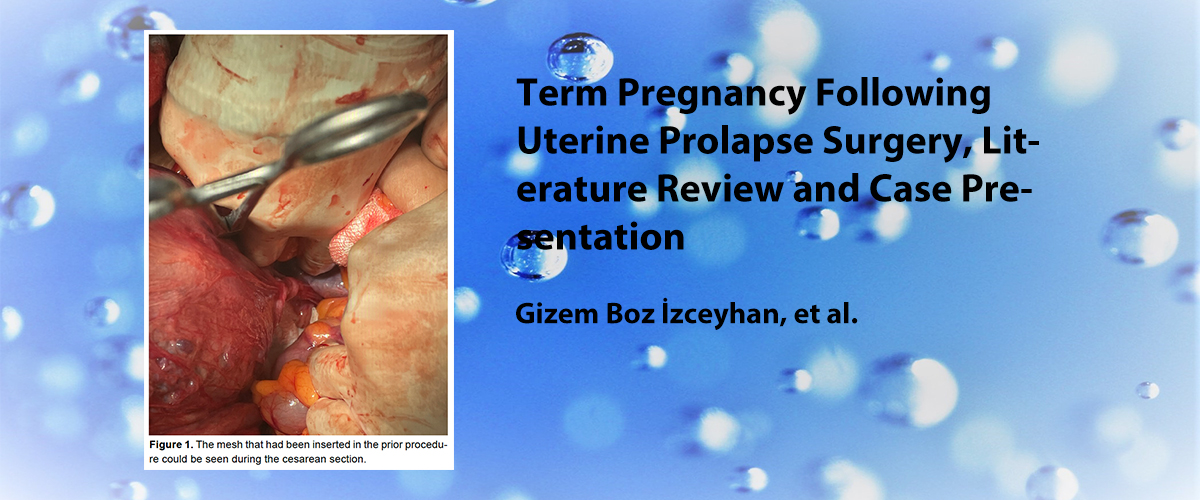
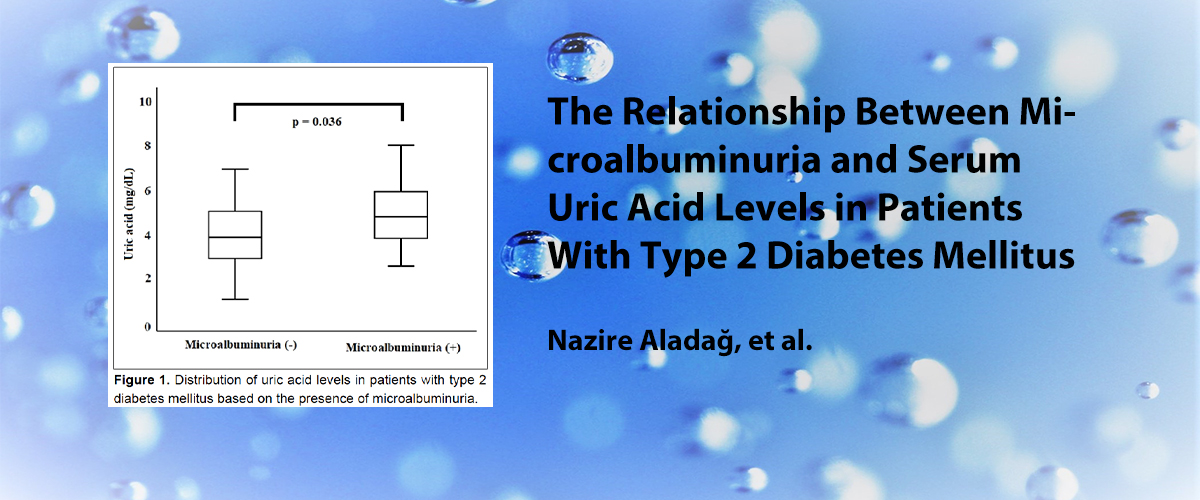
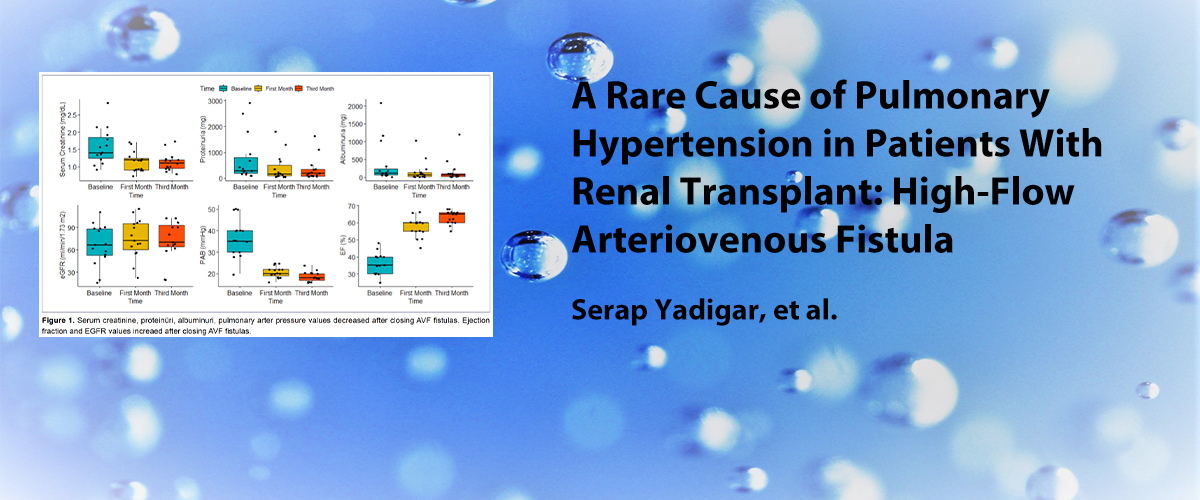
ISSN : 2587-0998
Sıçanlarda Böbrek Dokusunda Farklı Fraksiyon Şemalarında Uygulanan 12 Gy Radyoterapinin Yarattığı Akut Etkilerin Histopatolojik Olarak İncelenmesi
Hakan AkdereTrakya Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi, Ana Bilim Dalı, Edirne, TürkiyeGİRİŞ ve AMAÇ: Amacımız aralıklı verilen fraksiyone doz radyoterapinin böbrek hasarına etkisini incelemek.
YÖNTEM ve GEREÇLER: Sıçanlarda 6 gruba randomiz edildi: Grup 1: Kontrol; sham radyoterapi (n=5); Grup 2: Hipo-fraksiyone total abdominal radyoterapi (TAR); total 12 Gy (2 günde 2 fraksiyon) (n=4); Grup 3: Hipo-fraksiyone TAR; total 12 Gy (3 günde 3 fraksiyon; n=6); Group 4: Hipo-fraksiyone TAR; total 12 Gy (4 günde 4 fraksiyon; n=6); Group 5: konvansiyonel ayırma ile TAR; total 12 Gy (6 günde 6 fraksiyon; n=6); ve Group 6: konvansiyonel ayırma ile TAR; total 12 Gy (7 günde 7 fraksiyon; n=6).
BULGULAR: Hipofraksiyone gruplar 3 ile 4 (2.66±0.51) ve grup 5 ile 6 (1.83±0.40) arasında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark tespit edilmezken grup 2 (3.75±0.51) ile grup 34 ve grup 56 arasında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark tespit edilmiştir (p<0.05).
TARTIŞMA ve SONUÇ: Bu çalışmamız hipo-fraksiyone total abdominal radyoterapini, böbreklerde akut doku hasarına konvansiyonel radyoterapiye göre daha belirgin şekilde yol açtığını göstermiştir.
Acute Histopathological Response of Renal Tissues After Varied Fractionated Abdominal 12 Gy Irradiation In Rats
Hakan AkdereDepartment of Urology, Trakya University Faculty of Medicine, Edirne, TurkeyINTRODUCTION: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of fraction dose irradiation on kidney damage due to scattered radiation.
METHODS: Rats were randomized into 6 groups. Group 1: Control group, a sham irradiation (n=5); Group 2: Hypofractionated total abdominal irradiation (TAI), total of 12 Gy (2 fractions in 2 days) (n=4); Group 3: Hypofractionated TAI, total of 12 Gy (3 fractions in 3 days; n=6); Group 4: Hypofractionated TAI, total of 12 Gy (4 fractions in 4 days; n=6); Group 5: TAI with conventional fractionation, total of 12 Gy (6 fractions in 6 days; n=6); and Group 6: TAI with conventional fractionation, total of 12 Gy (7 fractions in 7 days; n=6).
RESULTS: There was no statistically significant difference (p>0.05) between the hypofractionated group sets of Groups 3-4 (2.66±0.51) and 5-6 (1.83±0.40). However, a statistically significant difference was found in the comparison between Group 2 (3.75±0.51) and the group sets of Groups 34 and 56 (p<0.05).
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The present study demonstrated that hypofractionated TAI leads to more prominent acute tissue damage in the kidneys than does conventional irradiation.
Sorumlu Yazar: Hakan Akdere, Türkiye
Makale Dili: İngilizce